Basics of linear regression
Linear regression is the statistical method that allows to find relationship between between $Y$ variable and $X$ variable.
To get valid estimates of linear regression, several assumptions must be valid.
-
Model should be linear in parameters.
-
None of the independent variables have linear relationship with any other independent variables. {i.e., no Multicollinearity}
-
None of the independent variables are correlated with mean of error.
-
Error term observation are independent to each other OR they are not correlated to each other. {i.e., no autocorrelation}
-
The errors in the regression should have conditional mean zero: $$ E[\varepsilon X] = 0 \(. The immediate consequence of the exogeneity assumption is that the errors have mean zero:\)E[\varepsilon] = 0 \(, and that the regressors are uncorrelated with the errors\). The exogeneity assumption is critical for the OLS theory. If it holds then the regressor variables are called exogenous. If it doesn't, then those regressors that are correlated with the error term are called endogenous, and then the OLS estimates become invalid. In such case the method of instrumental variables may be used to carry out inference. -
Error term has a constant variance. {i.e., no Heteroscedasticity}
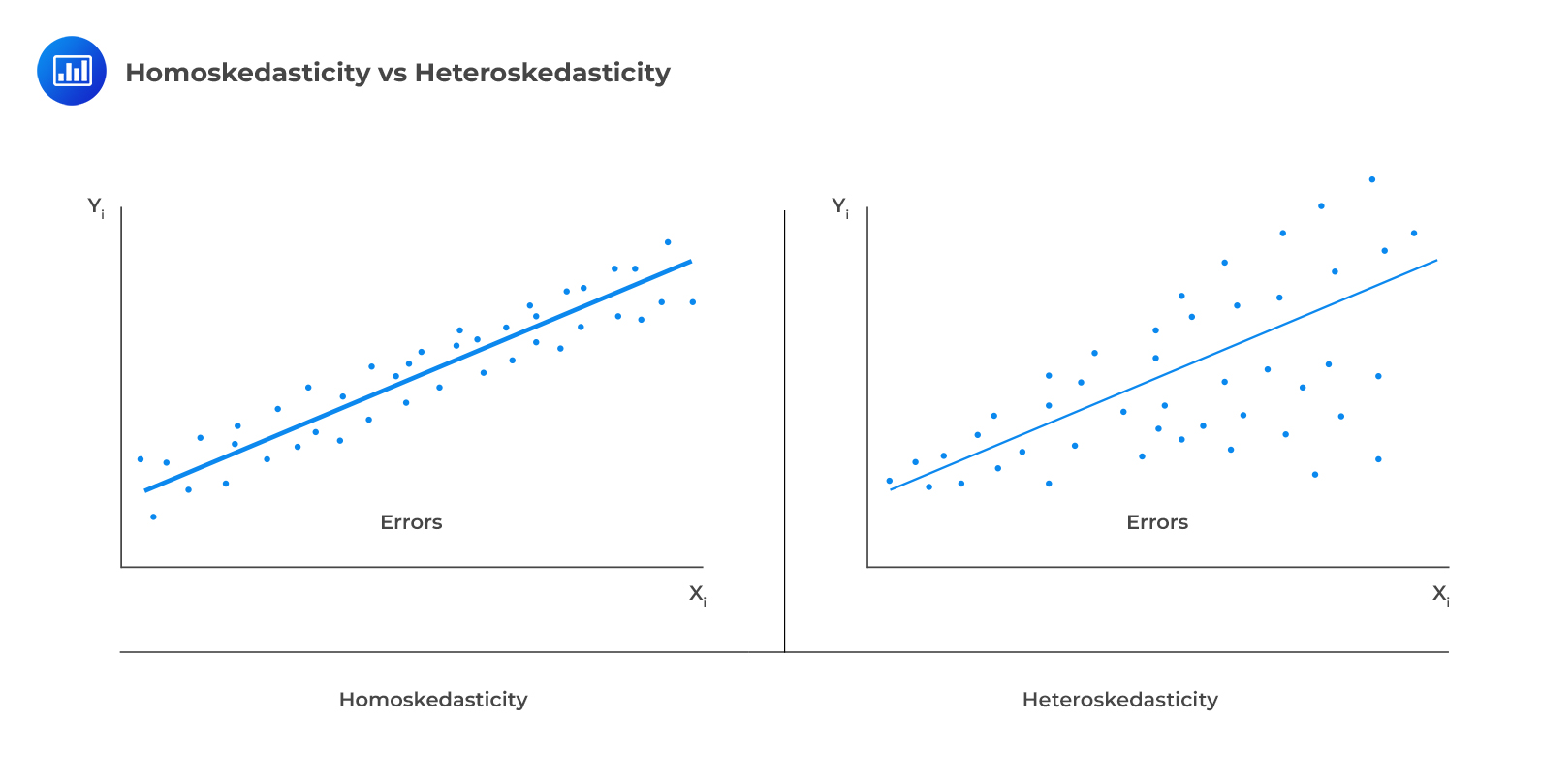
- The error term is normally distributed.
##